
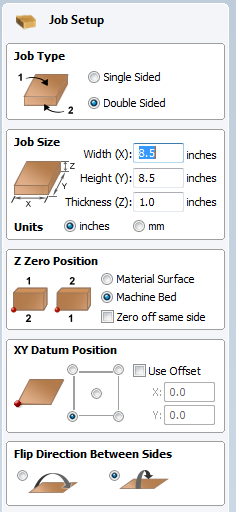

The Y axis should point along the short side of the rectangle (away from the FRONT plane on the View Cube) and the X axis should point along the long side of the rectangle (away from the SIDE plane on the View Cube). Z needs to be the up-axis from this point of view, so if you click on the arm of the Z axis, then click on any vertical line that's visible in the model, Z will become the up-axis. The Work Coordinate System (WCS) will also appear as an XYZ axis. SET WCS ORIENTATION: You should see a yellow box appear around the parts that are visible on the canvas. In this menu, you'll set the X,Y, and Z coordinates and establish the dimensions of the stock to be cut.Ģ. CREATE NEW SETUP: Next, click the New Setup icon under the SETUP menu. You'll see the toolbar change at the top of the screen with a new set of options.ġ. To create a machining setup, switch the workspace from MODEL to CAM. The first step in creating tool paths is creating a machining setup.
#ENROUTE 4 WOOD HOW TO#
With all the toolpaths finished, you'll learn how to post-process the data into a format that a CNC machine can read. You'll also learn about creating tabs to keep the pieces in place while the router is cutting. With all the pockets finished, you'll create a tool path to cut out the profiles of all the table pieces. It's good practice to do all the smaller cuts and drilled holes before the main contour cuts because they're less risk of pieces getting pushed out of place. The pockets on the underside of the table top will be the first cuts you make. This includes width, length, and thickness of the material as well as X,Y, and Z coordinates. In this part of the process, we'll set up the general parameters for our machining operations. CAM stands for Computer Aided Manufacturing- it's the process of translating the design into instructions that the CNC router can use. Now that your design is finished, it's time to get into the CAM environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
